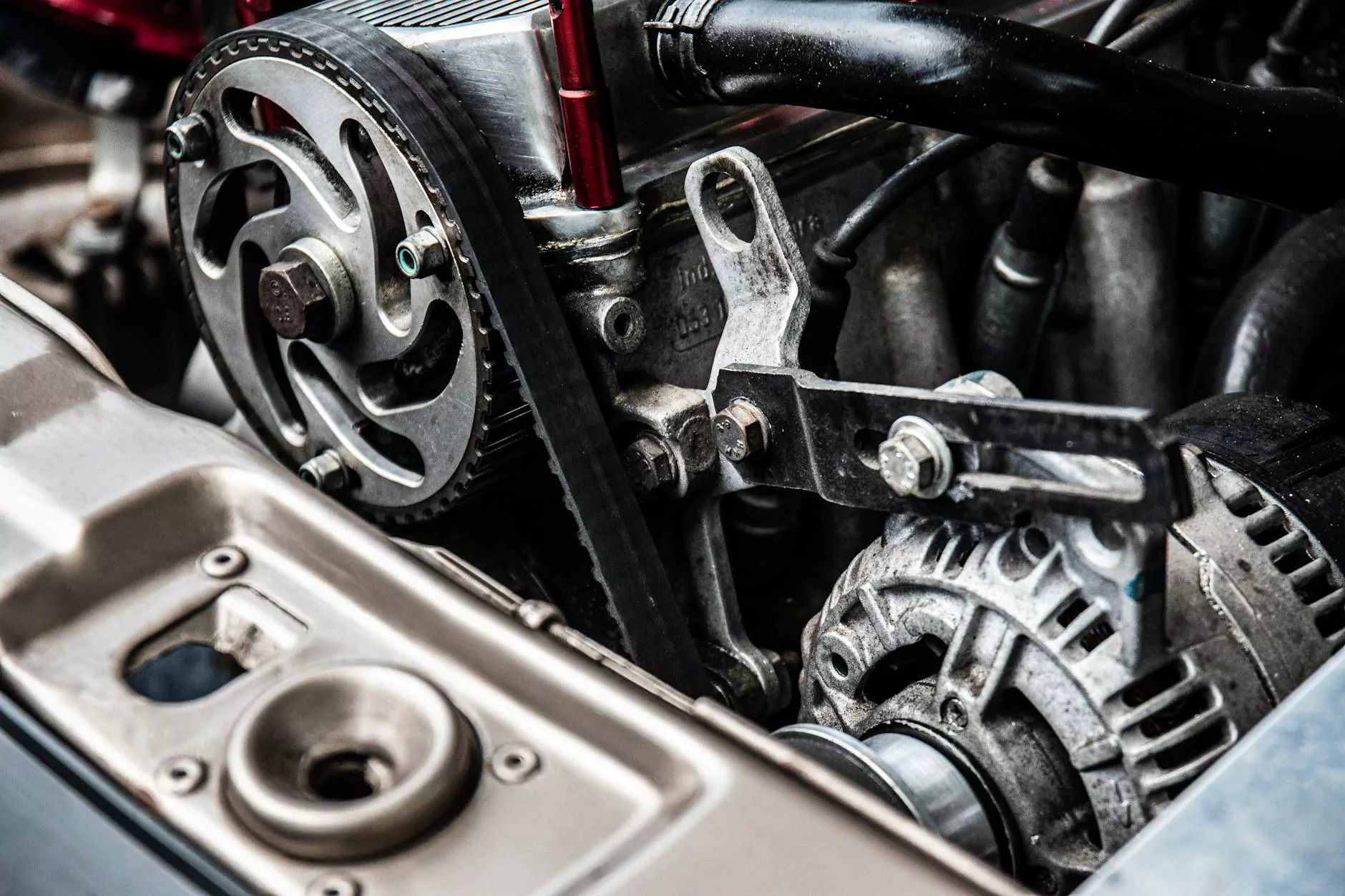
Understanding the Parts of the Piston Engine
The piston engine, an integral part of many diesel engines, consists of several components that work in unison to deliver power and efficiency. Understanding the parts of the piston engine is crucial for anyone involved in the maintenance or manufacturing of diesel machines. In this article, we will delve deep into each component, its functionality, and why it matters.
1. The Piston
The piston is the heart of the piston engine, moving up and down within the cylinder. Made typically of cast aluminum, the piston serves a critical function:
- Compression: It compresses the fuel-air mixture, aiding in efficient combustion.
- Power Stroke: The force from combustion pushes the piston down, creating mechanical energy.
Pistons come in various shapes and sizes depending on the engine design, with features such as piston rings that help enhance seal integrity and reduce oil consumption.
2. The Cylinder
The cylinder houses the piston and serves as its operational base. It is usually made of iron or aluminum and has an intricate design:
- Structure: Cylinder walls must be robust to withstand high pressure while maintaining a precise inner diameter.
- Cooling: The cylinder's design often incorporates cooling systems using water or oil to manage engine temperatures.
Any inconsistencies in the cylinder can lead to decreased performance and premature wear, highlighting its importance in the parts of the piston engine.
3. The Crankshaft
The crankshaft converts the linear motion of the piston into rotational motion, which ultimately powers the vehicle. It plays various roles:
- Power Transfer: As the piston moves, the crankshaft rotates, transferring energy to the transmission.
- Balance: It ensures smooth engine operation by balancing the forces exerted by the pistons.
High-quality crankshafts are critical as they are designed to endure substantial stress and strain throughout the engine's lifespan.
4. Connecting Rods
The connecting rods link the pistons to the crankshaft. This complex relationship is crucial for an efficient engine:
- Transmission of Force: They facilitate the transfer of force from the piston to the crankshaft.
- Support: They provide support and stability, allowing for proper axial movement.
Choosing high-performance materials for connecting rods can significantly enhance engine performance.
5. The Cylinder Head
The cylinder head covers the top of the cylinders and contains several vital components:
- Valves: These allow air in and exhaust out, playing a direct role in engine efficiency.
- Fuel Injectors: They help mix fuel with air for optimal combustion.
A well-designed cylinder head enhances airflow, improves combustion efficiency, and minimizes emissions, making it essential in the parts of the piston engine.
6. Valves
The engine utilizes valves that control the flow of air and fuel into the combustion chamber:
- Intake Valves: These valves open to allow the air-fuel mixture into the cylinder.
- Exhaust Valves: These valves open to expel exhaust gases after combustion.
Precision engineering in valves is crucial for ensuring that they open and close at the appropriate times, directly affecting the engine's performance.
7. The Camshaft
The camshaft is responsible for opening and closing the valves at the correct timing. It operates in sync with the crankshaft and is integral to valve timing:
- Timing: It ensures valves open and close at the right moments for optimal compression and exhaust.
- Accuracy: Accurate camshaft timing enhances engine efficiency and power delivery.
Modern engines often have variable valve timing systems that allow even better control over valve operation, improving performance across a range of speeds.
8. The Lubrication System
The lubrication system is essential for ensuring smooth operation of all moving parts within a piston engine:
- Oil Pump: It circulates engine oil to reduce friction and wear.
- Filters: They clean the oil, ensuring that only pure oil reaches critical engine components.
Regular maintenance of the lubrication system is vital for engine longevity, reducing the risk of overheating and component failure.
9. The Intake and Exhaust Systems
The intake and exhaust systems are responsible for bringing air into the engine and expelling combustion gases. Their design impacts engine efficiency:
- Intake Manifold: Distributes the air-fuel mixture evenly to the cylinders.
- Exhaust Manifold: Safely directs exhaust gases away from the engine.
A well-designed intake and exhaust system can lead to significant power gains by improving airflow and reducing back pressure.
10. Engine Block
The engine block is the foundation of the piston engine. It houses most of the components, providing structural integrity:
- Material: Typically made from cast iron or aluminum alloys for strength and durability.
- Crankcase: The section housing the crankshaft and lubrication system.
The engine block's design must accommodate various parts while facilitating efficient heat dissipation and mechanical integrity.
Conclusion
Understanding the parts of the piston engine is not just beneficial for mechanics or engineers; it greatly aids in enhancing the performance and longevity of diesel engines. Each component plays a unique role in the function of the engine, and when maintained properly, they provide powerful and efficient operation.
If you are looking for diesel engine parts or are seeking spare parts suppliers, consider visiting client-diesel.com for high-quality components to ensure your engine performs at its best.